Thanks to Outlook Anywhere, connection to Exchange Server can be established with 443 SSL port from any place with internet. We will examine how to use the Outlook anywhere feature with Exchange 2010. This feature was referred to as “RPC over HTTPS” in Exchange 2003. It was replaced as ” Outlook Anywhere ” in Exchange 2007/2010/2013/2016/2019, it was replaced as “Outlook Anywhere“. When we activate Outlook Anywhere;
- Users who use notebooks in the company will be able to use their outlook as if they are in the company, even if they take their computers home, without any settings.
- There will be no need for less secure connections such as POP or IMAP from outside the company.
- There will be no need to make a VPN to look at e-mails over Outlook.
There are 3 steps we need to do to use the Outlook Anywhere feature. First, we will activate the Outlook Anywhere feature over Exchange 2010. Then we will open the SSL(443) port over the firewall. Finally, we will enable the feature to be used with a small change on Outlook.
Note: The Self-Signed certificate that is automatically generated after Exchange installation is not a trusted certificate in the internet environment. To connect externally, an Outlook Anywhere connection must be established with a trusted certificate. Or, the certificate used in the internal network must be manually installed on the computer that will use this feature in the internet environment.
Activating Outlook Anywhere on Exchange
When we right-click on the server name in “Server Configuration –> Client Acess”, we start activating the feature by clicking “Enable Outlook Anywhere” as in the figure above.
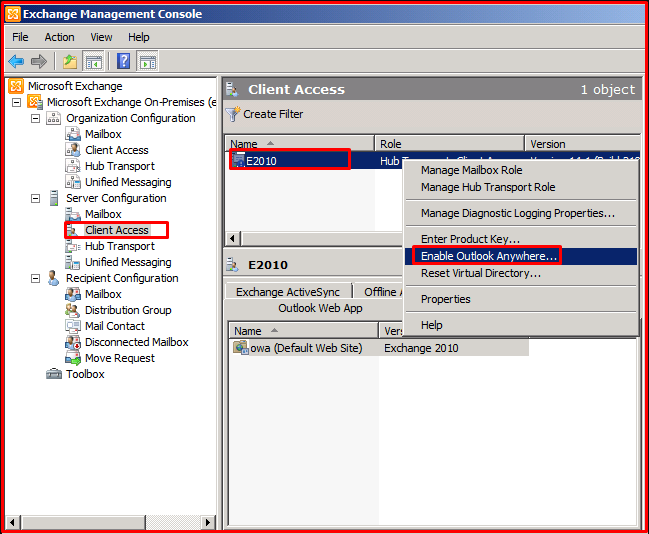
On the “Enable Outlook Anywhere” page, we write the external mail address as “External Host Name“. This is our outlook web address (OWA). Authentication occurs when users connect to Exchange Server with RPC. It asks how we want to do this authentication.

Let’s look at what the authentication methods here are;
Basic Authentication: In this control, every time the user opens outlook, it prompts for username and password. Username password information is sent openly over the network. This method is not very reliable. This option can be used if the computer is not in the domain or if the firewall/ISA only supports basic authentication.
NTLM Authentication: After the user logs on to the computer, he connects to the Exchange Server with that user-name password information and uses the Outlook Anywhere feature. It is a more reliable mechanism. Username-password information is never sent over the network. Authentication takes place in the form of a kind of matching.
Negotiate Ex Authentication: This feature is an authentication mechanism that Microsoft will use in the future. If this option is selected, authentication will fail.
We choose “NTLM Authentication” because there is no firewall preventing me from using “NTLM Authentication“. If your firewall or load balancer device such as f5 supports the “SSL Offloading” feature, you can select the “Allow secure channel(SSL) offloading” feature. “Outlook Anywhere” will not work properly if it is not supported and you select this feature. Thanks to “SSL Offloading, “ firewall or load balancer-style devices terminate the “SSL” request from the outside, open a new connection, and forward it to the Exchange server. It can also do the opposite of the same process. These devices have the encrypt-decrypt feature. At the same time, since all “SSL” operations are done on the device, it directly affects the performance by reducing the “CPU” usage on the “SSL” server.




