ElasticSearch is a Search Engine preferred by companies working with BigData, that is, for content search, data analysis, queries and suggestions, especially due to its performance capabilities, strong and flexible features. Examples of large companies using ElasticSearch are LinkedIn, Stack Overflow, Foursquare, GitHub and Amazon.
In order to store and analyze big data (Big Data) correctly, we first need to be able to see our needs well. If we need a full-text search between large data blocks, then Elasticsearch may be the right choice for us. Elasticsearch searches through indexes instead of directly searching through text and produces results very quickly. In addition, it can perform statistical analysis and score on the queries.
Elasticsearch Infrastructure
Elasticsearch is an open-source project, written entirely in Java language, with a distributed architecture. The search engine is based on the search engine Apache Lucene project. Lucene project mostly provides indexing and searching of plain texts which we call unstructured. Elasticsearch, on the other hand, provides the data structure we call structured on the Lucene infrastructure to index and search certain documents. Basically, every document kept on Elasticsearch is a JSON object and it has a unique id that distinguishes that document from other documents.
How does Elasticsearch make Searches Over Text?
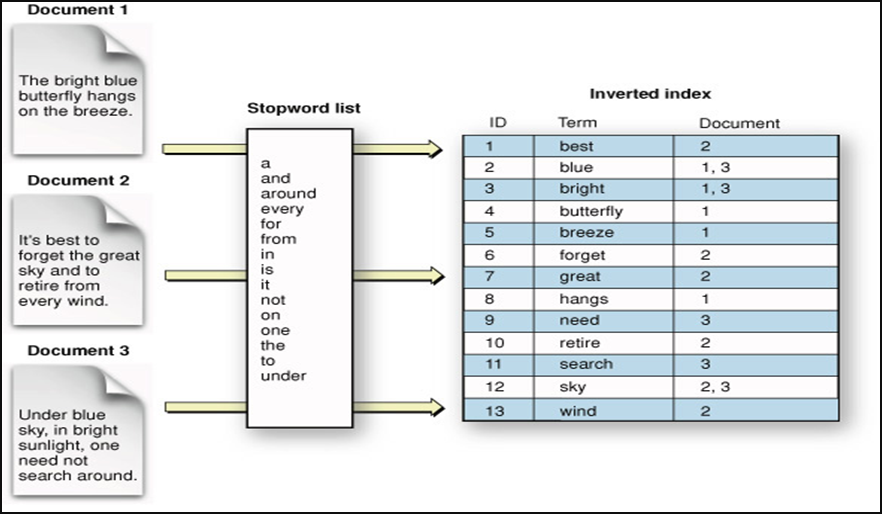
When we save data to Elasticsearch, the fields we specify in the data are indexed using the Apache Lucene infrastructure. Elasticsearch indexes in which document (row) a word occurs while saving the data. Then, when we want to search for words, instead of searching all data, the results are found quickly on the index list created earlier. For example, when we want to search for the word keeper in the document below, we quickly get 1,4,5 result from the index list.

Benefits of Elasticsearch Framework to Us
SPEED
First of all, we can say that the most important feature of the elasticsearch framework is very fast. Basically, it can hold all the data that a relational database system can hold, and allows you to query these data much faster than a database system. It uses special index structures that can hold numerical values, geographical values, dates and texts to provide this speed.
Basically, you assign your data consisting of trillions of rows to elasticsearch in JSON format, and you can access your data in milliseconds with the correct configuration and easy-to-use API.
SCALABILITY
Elasticsearch can be run on a laptop if you want, or you can run it on a server. Cluster installations are made completely automatically by the elasticsearch infrastructure.
Moreover, communicating with an elasticsearch installed on your laptop and communicating with an elasticsearch cluster consisting of thousands of servers is just as easy. Elasticsearch also automatically decides how it should keep data and indexes for you.
Easy to Use
Elasticsearch can be used very easily thanks to the REST APIs it provides. Moreover, you can use it with many programming languages such as Java, C #, Python, Javascript, PHP and Ruby with special libraries written for each language.
Features of Elasticsearch
- It is open source. It is based on Java.
- It is based on Apache Lucene (Shared and Replica concepts are also valid in ES).
- The data storage format is document-oriented, not relational.
- It can do automatic mapping according to the data type.
- It has a cluster structure and its cluster structure is very simple.
- It can work in a distributed and scalable structure.
- It allows for analyzing real-time data.
- It has concepts such as Type, Fields, Documents, Fields, Indicates, Full-text search and Index.
- It can be used with all programming languages as it provides service over RestfullAPI.
- It can be used with Kibana, which can monitor Elasticsearch and Logstash tools to host logs.
- It offers high accessibility in itself.
- It promises fast installation and easy configuration.
- It is quite easy to transfer data to Elasticsearch.
- There are structures such as River for data transfer.
- It indexes documents as JSON.
- It also makes it possible to transfer to ES from NoSQL databases such as HBase, Cassandra and MongoDB.
Elasticsearch Components and Basic Principles
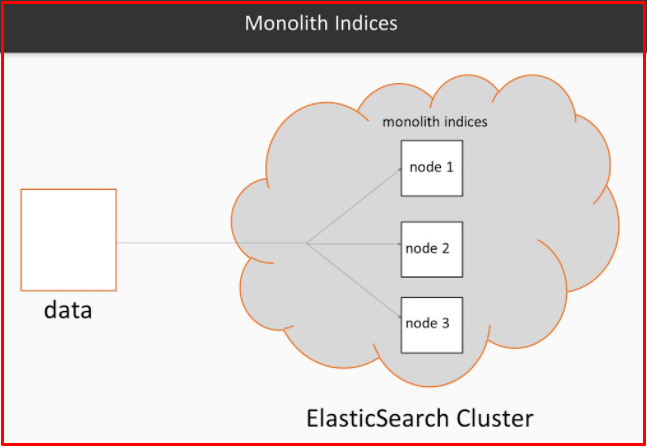
Indice
Indice concepts are used in Elasticsearch instead of Databases in classical relational databases. An Elasticsearch cluster can contain multiple indices (databases).
Type
For tables in relational databases, ES uses the “Type” concept. An indice can contain more than one type (table).
Document
They are represented in Elasticsearch as Rows Documents in relational databases. Each type has more than one document.
Field
Columns in classical databases are qualified as Fields in Elasticsearch. Each document has more than one field.
Full-text search
It is the name given to quickly access the result found by searching any keyword among text documents taken from any source, and documents matching the keyword.
For example, suppose you search for the name of a scientist on wikipedia.com and read the articles about it.
When you type Nicola Tesla in the search bar of Wikipedia, instead of searching all the registered articles to find the articles about it, it is the structure that allows you to go to the index with the text of Nikola Tesla’s name among the previously indexed data and quickly return your results.
Index
Each record added to Elasticsearch is configured as a JSON document. For each word in your documents, there is an indexing system that keeps the information on which document or documents it contains. You can think of it as a kind of database. Like the order in the data in the database, Elasticsearch’s indexes are also organized in JSON format.
Mapping
While indexing the data, we need to show what type of data it is. In other words, when indexing a word, it is the process where the data type (string, integer, boolean) of the word is defined.

RestfullAPI
REST is an architecture related to client-server communication. Restfull services can return many different types of responses (JSON, XML, CSV, HTTP) between client and server. RestfullAPI is an API that uses these services.
Near Realtime
Elasticsearch runs at near real-time speed. The reason it is called “near real-time” instead of real-time is that it indexes a document with a slightly different latency than real-time. (This period is usually a one-second delay.)
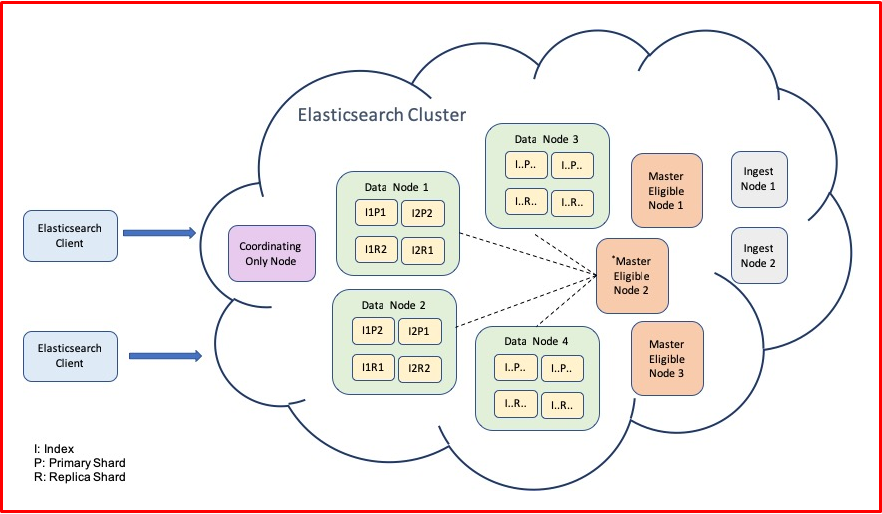
Cluster
It can be called a cluster or collection of nodes consisting of multiple Node that hold all your data together and executes all indexing and search capabilities.
A cluster is defined by a unique name, “elasticsearch” by default. This naming can be changed optionally. Naming is important because a node can only be part of a cluster. If the node is set to join the cluster with a cluster name, the correctness of these name definitions will be needed.
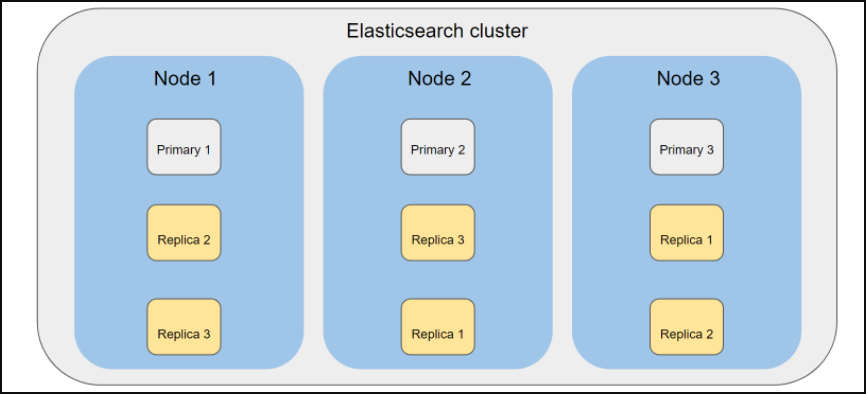
Node
It is the name given to a single server. Each of the machines is where data is stored. The indexing and search capabilities of clusters are realized through these nodes. As in the naming logic in clusters, nodes are initially assigned a unique id (Universally Unique IDentifier (UUID)).
These names are very important for the management of information exchange between nodes. These names can also be changed if desired.
By default, each node is set to run in a cluster named “elasticsearch”. If you want which node to go to which cluster, you must direct it to that cluster name.
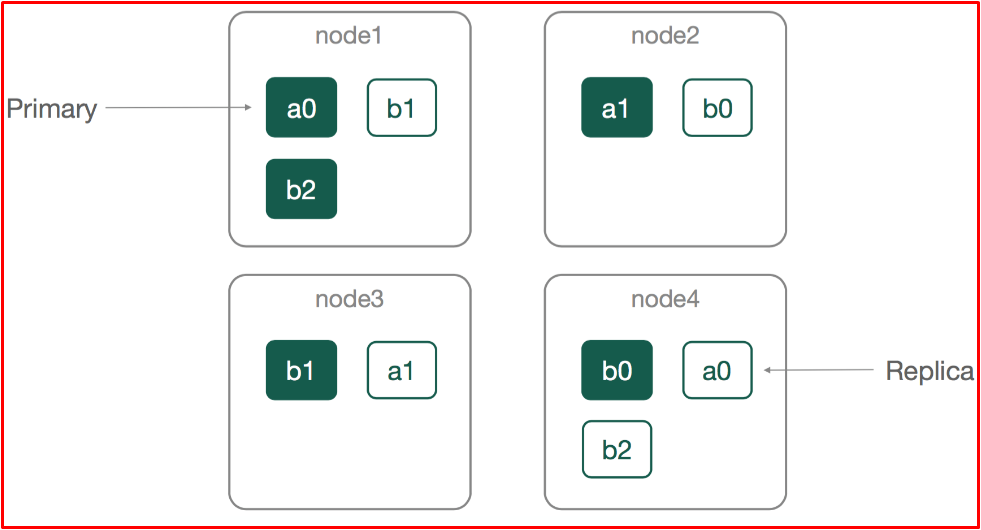
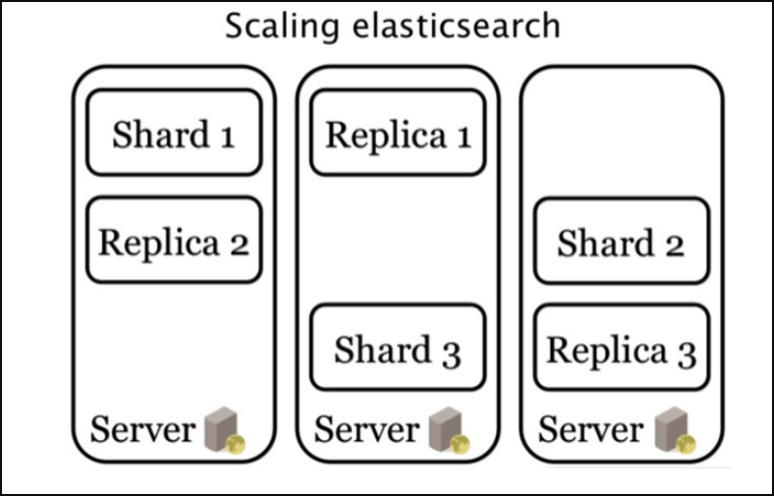
Shard
You may not have enough hardware capacity to index millions of documents at a time. Suppose you have to index 2TB of data at a time, so when you want to do indexing with a single node, you may be faced with a full disk capacity or an extremely slow indexing speed. To prevent this, there are concepts of Shard and Replica. An index to be made is divided into shards on a node again. You can use these shards according to your wishes. There are two main purposes for using Shard architecture. These,
It allows you to distribute and parallelize transactions across multiple nodes. Thus, performance increases.
It allows to divide and scale the content volume horizontally.
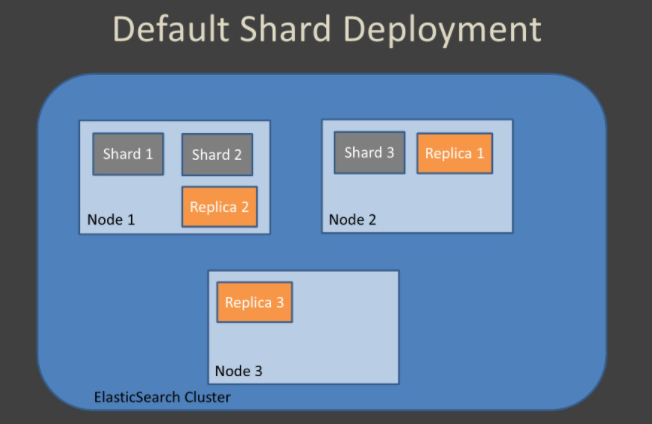
Replica
There is a replica-shard structure that allows one or more copies of index shards to be created in case the shard becomes disabled. Replica of a shard should not be hosted on the same node. When a node crashes, it is essential to have backups of the shards on that node in other nodes to prevent data loss. It is not obligatory to determine Replicas and Shards from the beginning in Elasticsearch. You can set optional. The sampling scheme of splitting Shards and Replicas into different nodes is as follows.