One of the security features that come with Windows 10 1903 is that we can use a “sandbox” in our operating system. Thanks to virtualization technologies, we have written very nice features such as a Credential guard or devices guard with Windows 10 before. Windows Sandbox is a feature that allows you to build a sandbox container using virtualization technology in 1903. This container will be running a separate instance of Windows 10 where you can install apps, use the internet, and test all kinds of things. In fact, although it seems like activating the hyper-v role on Windows 10 and installing a Windows 10, the beauty of it is that it is extremely useful. Because when you are done, the moment you close the sandbox application, this copy of windows 10 is deleted. In this way, an unnecessary system resource is not used. An excellent feature to test a suspicious application or code before running it.
Note: First of all, the Windows 10 version 1903 and the “Virtualization Technology” feature must be turned on in the BIOS.
Note: If you want to enable it in the virtual machine, you must first run the following Windows PowerShell command.
Set-VMProcessor -VMName -ExposeVirtualizationExtensions $ true
Installing the Sandbox Feature
You can install the sandbox feature in two options.
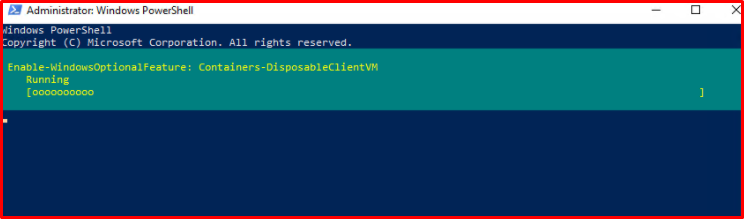
- With the command below, you can activate the Sandbox feature using a single line PowerShell command.
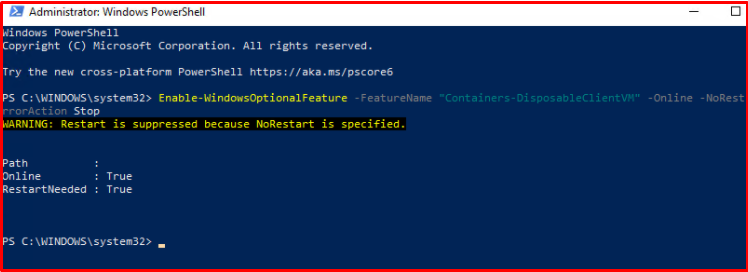
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -FeatureName “Containers-DisposableClientVM” -Online -NoRestart -ErrorAction Stop
- You can also install the Sandbox feature using the interface as below.

Using Sandbox Software
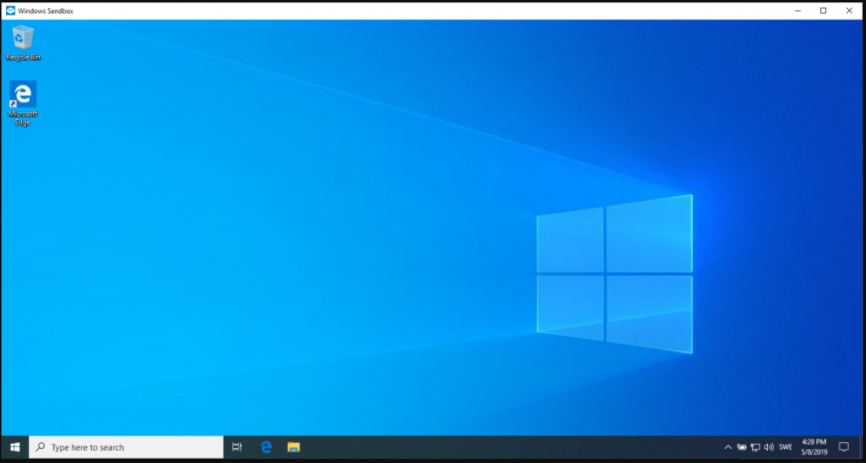
You can see the Windows Sandbox application by searching the Sandbox software in the Start menu or by scrolling down to the lower section in the menu.

When you click on the application, you will see a new Windows 10 desktop. You can see in the example like a new virtual machine.
You can move the product you want to analyze into the sandbox with copy and paste logic.
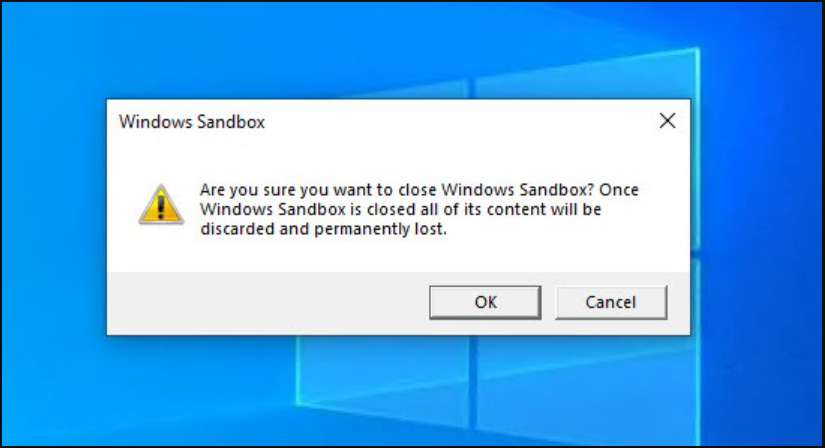
It is really a great alternative for both security and pilot deployments such as patch distribution. When you are done, you will receive a warning as below when closing the program. This is a warning that all changes and data we make will be deleted. Any changes you have made will be deleted. It will also return the received resource back to the system.
Resource consumption, on the other hand, consumes only an average of 100MB of ram while there is no operation on the machine. However, at the end of the day, you will see that the more load you put on this sandbox application, the more resources it consumes.





