Every website on the Internet has an IP address. For example, if you type https://216.58.206.206/ in the address bar in the browser, you will go to https://www.google.com. You can think of these IP addresses as phone numbers. The IP address of every site, even every modem that connects to the internet, is unique, just like the phone number.
Of course, IP addresses are difficult to remember. If there was no DNS, you would need a software just like the phone book to remember the IP addresses of dozens of websites you entered frequently. This is where DNS technology comes into play.
The technology that converts easily remembered website addresses to IP addresses, “DNS”.
It is expressed as “Domain Name System”. It is a system used to convert hostnames that can grow up to 256 characters to IP. The hostname, also known as the fully qualified name, indicates both the computer name and the internet domain where the computer is located. DNS allows machines to communicate with hostnames on the internet by resolving the IP address of a given machine name.
DNS History
Until 1984, there was no such thing as DNS. Until that year, the name-IP analysis was done with a text file called HOSTS. The names and IP addresses of computers on the Internet were recorded manually in this file. Each computer on the Internet had a copy of this file. When a computer wanted to reach another computer, it was examining this file, if the file contained a record of that computer, it received its IP address and communicated.
In order for this system to work well, the contents of the HOSTS file had to always be up to date. To ensure this, copies were made periodically by connecting to Stanford University in the USA, where the original file is kept.
But as the number of computers on the Internet increased, the size of this file started to reach extraordinary dimensions. Connections made by computers on the Internet to copy the file began locking the computers at Stanford.
Another disadvantage of using a single HOSTS file is that since all computers are located at the same level, it was necessary to ensure that a computer name does not have another equivalent on the whole Internet.
Because of these problems, internet authorized bodies produced DNS in 1984. DNS both made the computer database into a distributed structure and provided a hierarchical structure between computers.
In DNS, distributed database, computers were classified according to the institutions they belong to where they are located. For example, a list of computers in Turkey (.tr domain) was holding Turkey responsible for a DNS server machine. Thus, it was not necessary to keep the information on all computers in the internet environment in one place.

How Does DNS Work?
The DNS system consists of name servers and resolvers. Computers organized as name servers keep IP address information corresponding to hostnames. Resolvers are DNS clients. DNS clients contain the addresses of the DNS server or servers.
When a DNS client wants to find the IP address for a computer’s name, the name refers to the server. The name server, that is, the DNS server, if there is such a name in its database, it sends the IP address corresponding to this name to the client. Records must be entered manually in the DNS database.
Internet addresses are first divided by country. Expressions such as tr, de, uk at the end of the addresses indicate the country where the address is located. For example, Turkey “tr“, for Germany “de” and also for England, “uk” shows. A country tag is not used for US addresses because the country that creates DNS and similar applications is the USA.
After the Internet addresses are divided into countries, they are divided into more sub-sections such as com, edu, gov. These expressions correspond to top-level domains in DNS. Top-level domains are as follows:
Com: Indicates commercial organizations.
Edu: It shows educational institutions.
Org: It shows non-commercial institutions that are not affiliated with the government.
Net: It shows the networks that act as the Internet backbone.
Gov: It shows the government institutions.
Mil: Indicates military institutions.
Num: Shows where you can find phone numbers.
Arpa: It shows the places where the reverse DNS query can be done.
Field names are used in a structure called tree structure and branching according to a certain rule. Except for America, addresses in all countries connected to the internet end with the country code of that country’s ISO3166.
Common DNS Server Software
As explained above, there is software with different platforms and qualities such as the most widely-used DNS server software BIND, then Microsoft DNS Service, PowerDNS. Considering the amount of data they process, they consume very little resources. In this way, tens of thousands of DNS Zones can broadcast even on a very old and primitive server with low CPU power. For a detailed comparison, you can check the related DNS Server software link.
Why Change DNS?
If you want to change the server, change the IP address of your site and use a distributed service, you can do this through DNS records.
The main reason for wanting to change the DNS address is; is to want to change the IP address of a website. However, DNS changes are also made to access sites that are prohibited by the courts.
The easiest way to block access to a site is DNS-based blocking. When you use DNS of any internet service provider that provides service, when you request IP information to access the banned site; This request is rejected by the DNS server you are using and the IP address in question is not shared with you. Instead of the message “We do not want to share this IP address with you”, you will see the message “Access to this site has been blocked with xxxx decision”. In fact, the page you see is nothing more than a mask page to which you are directed.
Note: If you are not satisfied with your internet connection speed or if you want to be protected from possible cyber-attacks (provided you use services like Cloudflare), you can change DNS.
How to Change DNS Settings?
1.Changing DNS in Android Operating System
Changing DNS on mobile devices using the Android operating system is quite simple. You can change the phone or DNS settings by following the steps below.
Click on the “Settings” menu.
Then click the “Wi-Fi” option.
Select the “Wireless” option.
Click on the “Manage Network Settings” menu.
Select the “Show Advanced Options” option.
From the “IP Settings = Static” menu, edit the DNS records as you want.
If you do not want to deal with all this, you can download THIS application by connecting to the Google Play Store.
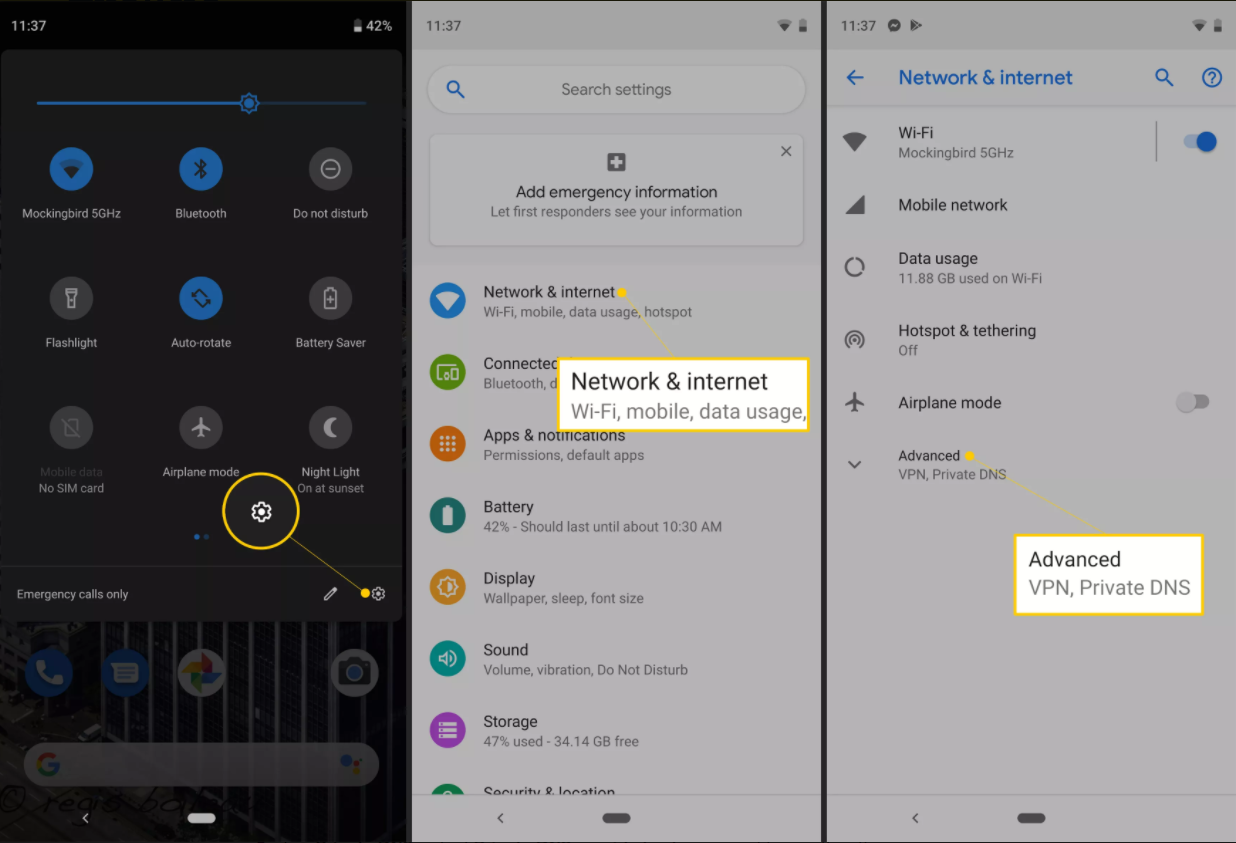
2.Changing DNS in IOS Operating System
Changing DNS on iPhone phones using the IOS operating system is also very simple, just like Android phones. If you follow the steps below, you can change the DNS settings of your iPhone brand phone in less than 2 minutes.
Enter the iPhone “Settings” menu.
Find and click the “Wi-Fi” option.
Click on the Wi-Fi network you are connected to.
Next to the Wi-Fi network you are connected to, touch the blue “i” ie “info” text.
Click on the “DNS” section in the menu that opens and edit this field by typing in the DNS address you want.
When you exit the menu by clicking on the “Wi-Fi” text in the upper left and showing an arrow to the left, you will have edited the DNS records.
3.Changing Mac DNS Settings
System Preferences> Network> Location: Add New> Advanced> DNS tab to add records.
4.Changing DNS in Windows Operating System
It is also possible to change DNS on your desktop computers running the Windows operating system. For this, simply follow the steps below.
Go to the “Network and Sharing Center” section.
Select the “Change Adapter Settings” option.
Click on “Ethernet Feature Settings”.
Change your DNS records as you wish in the “Internet Protocol Version 4” section.
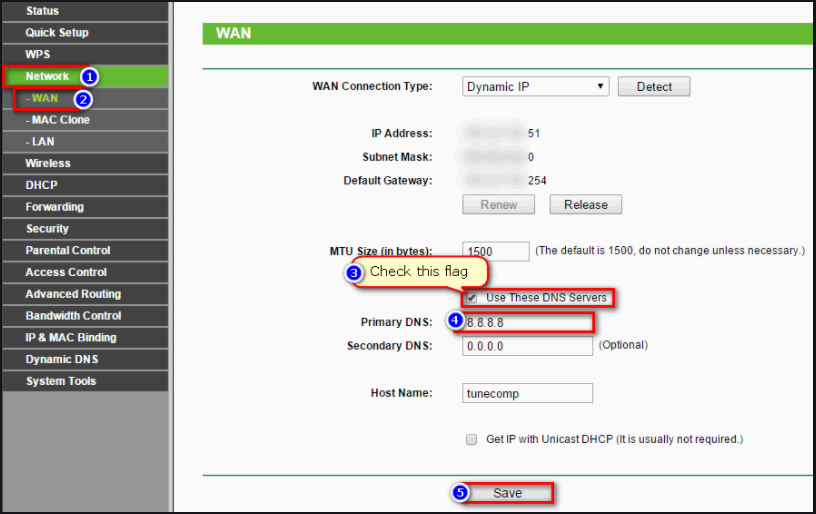
5.Changing DNS in Linux Operating System
In Linux, DNS addresses are kept in the resolv.conf file under the / etc directory.
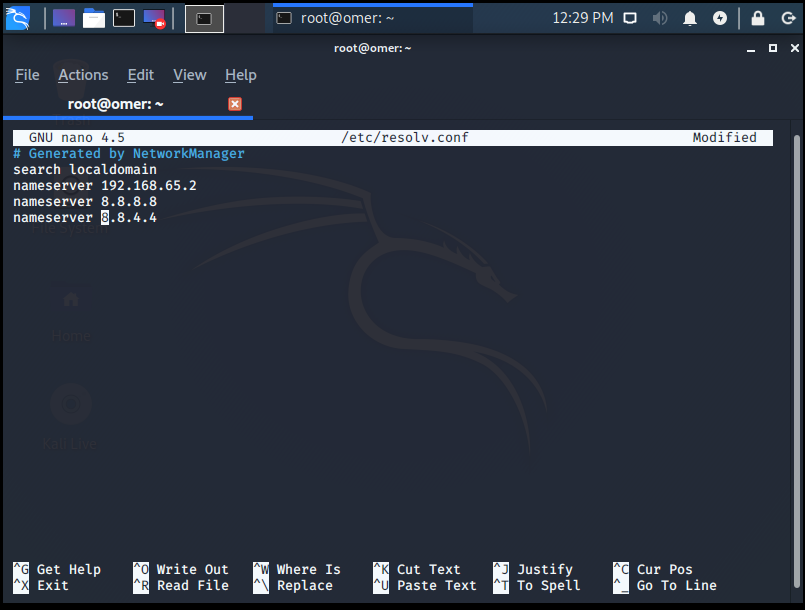
We opened the resolv.conf configuration file with the nano editor by getting root privilege with sudo.
We see our default DNS address 127.0.1.1, we will replace it with Google’s DNS of 8.8.8.8 /8.8.4.4. For this, we will INSERT our editor by pressing “ctrl + x” and y key.
sudo nano /etc/resolv.conf
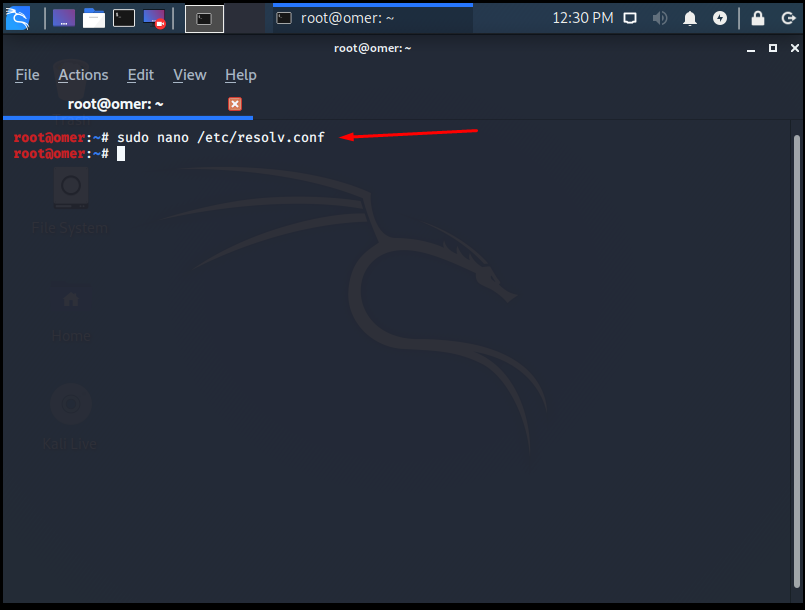
Note: This process will be deleted when we restart the computer.
sudo chattr + i /etc/resolv.conf
We will make our transaction permanent by giving the command. Chattr + i is the command to lock our file.
How to Change DNS Settings for a Domain Name?
You can change the DNS settings for your domain name by going to the “DNS Zone Editor” or “DNS Domain Editor” section in the hosting panel.
DNS Record Types
In the DNS domain editor mentioned above, the following parts, namely “DNS Record Types” can be edited.
A Record
The basic DNS record type used to associate a domain address with an IP address. They only point to IPv4 addresses.
CNAME Record
A CNAME record is also called “Alias Record”. To use this record, you must have made a correct “A Record”. To forward your subdomain addresses to a different IP address, simply edit the CNAME record field.
MX Record
The area where you can process information related to your mail traffic is referred to as “MX records” or “Mail Records”. You can enter the addresses of your e-mail servers in this field and specify the priority order.
DNS TXT Record
It is a type of registration that is not used very often. “SPF” records named “Sender Policy Framework” are kept here. If the purpose of SPF is; To prevent e-mails sent via fake e-mail addresses.
AAA Record
In fact, it is a type of record that does exactly the same thing as “A Record”. The only difference is that it matches the IPv6 record with the domain name.
NS Record
It is an abbreviation of the word “Name Server”. With this record, DNS servers on the same network are quickly notified of each other. Also, you can determine the name of the current server for your domain name, thanks to NS records.
SRV Record
Every special service on the servers; address (location), port and protocol information is available. This information is kept in the SRV record. When this information is requested by any client, the relevant information is provided by checking the SRV record.
What is Open DNS?
Essentially Open DNS; It is a technology company serving in the state of San Francisco in the United States. The service it provides is actually; It is about delivering a faster and more privacy online internet experience. With the proxy service offered by Open DNS, you can have a faster internet experience and access banned sites.
Some of the services offered by Open DNS to the end-user are free. With Open DNS, it is possible to control the internet access of the devices in your home network and to block access to the sites you want.

DNS Zone Files and Record Types
There are various files and record types on the “DNS Zone”. These are as follows:
named.boot: the first file read by the program when the DNS starts up; It is a “named” file with a .boot extension. It is also a configuration file named.boot; It is located under the “/etc” directory. namaed.boot; Tells how to access other configuration files in the DNS Zone.
named.local: It is a file used to determine the address of the machine where the DNS server is located. The address of the machine in question is called “loopback”.
named.ca: This file contains the addresses of the machines called “root server (.)”.
named.hosts: This file is the “secondary domain name” or the file containing the addresses of the machines in the secondary domain running DNS. This means that all computer addresses running on the ultimate DNS server you go to are in this file.
named.reserve: This file with the extension .reserve, which is similar in structure to the “named.local” file, with the most simplified expression; It converts the IP address of the site you want to go to the domain name.
Common DNS Server Software
The most common DNS Server software; It is software with the abbreviation “BIND” named “Berkeley Internet Name Domain“. This software is the head of all DNS Server software. As an alternative to this software, software and platforms such as PowerDNS and Microsoft DNS Service can be used.
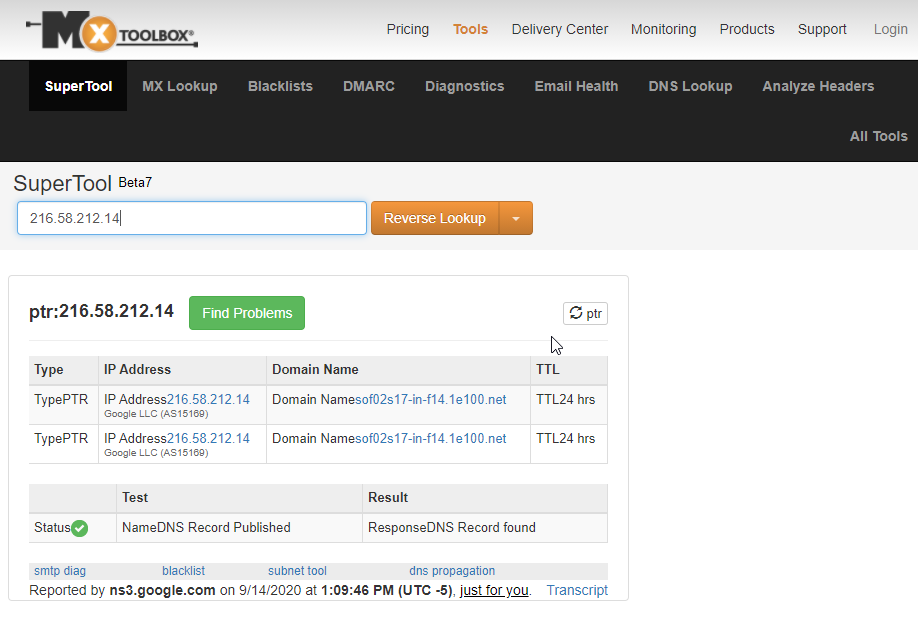
Reverse DNS Nedir?
Asıl adı “RDNS” ve “Reverse Domain Name System” şeklinde ifade edilen teknolojinin piyasadaki ismi “Reverse DNS” olarak geçmektedir. Aynı zamanda “PTR Kaydı” ismi ile de bilinir.
Reverse DNS aslında A kaydının tam tersi işlemi yapar. A kaydı, domain adresinizi bir IP adresi ile eşlemekte idi. Reverse DNS ise bir IP adresini bir ip adresi ile eşlemektedir. Üstelik A kaydı ve PTR kaydı, birbirinden bağımsız olarak çalışmaktadır. IP adresi A kaydında farklı bir domaine, RDNS kaydında farklı bir domaine eşlenebilir.
RDNS kayıtları en çok e-posta alışverişleri esnasında kullanılır. Size bir e-posta geldiğinde RDNS kontrol edilir ve e-postayı gönderen hesabın aslında hangi makinada olduğu tespit edilir. Eğer RDNS kaydınız yoksa; Gmail, Yahoo, Yandex, Hotmail gibi lider e-posta sağlayıcı firmaların hesaplarına elektronik posta yollayamazsınız.
RDNS kaydı için sıradan bir hosting panelinde düzenleme yapama imkanı bulunmamaktadır. Aslında bir sunucu DNS servisi sağlıyor ise mantık olarak “DNS Zone” üzerinden bu kaydın düzenlenmesi gerekir. Fakat ISP firmaları ve hosting sağlayıcılar, bu kaydı sadece kendileri düzenlemeyi tercih etmektedir.
Sitenize ait bir PTR kaydı olup olmadığını aşağıdaki adresten kontrol edebilirsiniz.
https://mxtoolbox.com/