VLAN was implemented by IEEE. It stands for Virtual Local Area Network. It works at Layer 2 of the OSI. Using VLAN technology, you can logically group network users and resources on a local area network (LAN) and assign them to ports. These logical networks are split broadcast domains. Since each VLAN receives only its own broadcast after VLAN configuration, broadcast traffic is reduced and bandwidth is increased. When it is desired to create a different VLAN on the LAN, the free ports of the switch can be used. In this way, you save on network investment.
Segmenting the network using VLAN can make it easier for users to manage. You can configure access permissions (access-list) more easily. It helps us in solving possible network problems.
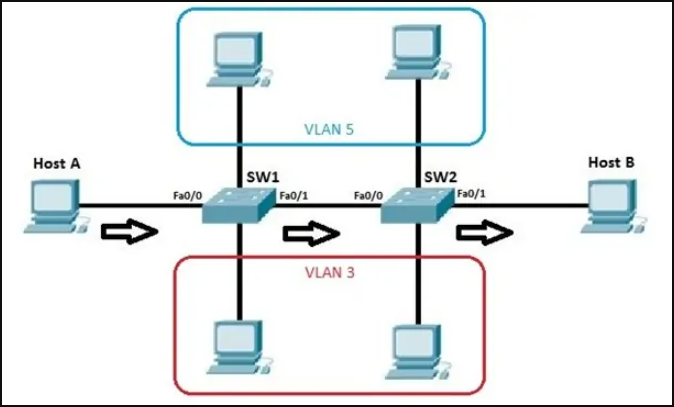
For example, including a guest user in the system network may not be healthy in terms of security. For this reason, it will be safer to take the guest user to the internet environment over a bent network isolated from the system. This is done by partitioning the network, that is, by configuring the VLAN. In a network using VLAN, users in VLAN can only communicate with each other, they cannot communicate with users in a different VLAN.
VLAN Types
Vlan consists of 5 types. You can see the Vlan types below.
-
Data VLAN
It is configured to carry standard traffic. Simultaneously, audio or video-based traffic can be transported. For example, user-generated internet traffic. Another name is User VLAN.
-
Default VLAN
In the default VLAN configuration, all ports on the switch are automatically included in the default VLAN when the switch is started. If the switch ports are connected to the Default VLAN, these ports are included in the same broadcast domain. All devices connected to this switch can communicate with each other.
-
Native VLAN
Local VLAN is the VLAN assigned to the “Trunk” port. A trunk port supports traffic without any VLAN tags and traffic generated by multiple VLANs. The “Trunk” port forwards traffic not coming from any VLAN to the local VLAN.
-
Management VLAN
It is a VLAN configured to manage the switch. Once an IP address or subnet mask is assigned to the management VLAN, this switch can be connected via HTTP, Telnet, SSH or SNMP.
-
Voice VLAN
It is a VLAN that is configured to pass only voice traffic over it. Voice VLAN is frequently used because voice transmission is important for institutions and individuals. In voice VLAN, an IP phone is used for voice transmission.
VLAN Definitions
VLANs are distributed among the connected switches. The packet received by the switch fabric is sent to the ports assigned to the VLAN it belongs to, with the method called “frame tagging”. The switch fabric is a group of switches that carry the same VLAN information. There are two kinds of connections in the Switch world. These are Access links and Trunk links. If we look at these links;
Access links: A link that belongs to only one VLAN. The device connected on the access link operates on the assumption that it is connected to a broadcast group, independent of the relationships between VLANs and the physical network. Switches remove the VLAN header on the packet before sending it to the device connected with the access link. The packets sent by the devices on the access link cannot talk to devices outside their VLANs unless they are routed by a router or another layer 3 devices.
Trunk links: It can carry multiple VLANs on it. A trunk link can be made from one switch to another switch, a router or a server. It has support only on Fast or Gigabit Ethernet. Cisco switches use two different methods to recognize the VLANs on the trunk link: These are; ISL and IEEE802.1q. Trunk connections are used to carry VLANs between devices. They can be formatted to carry all or some of the VLANs.
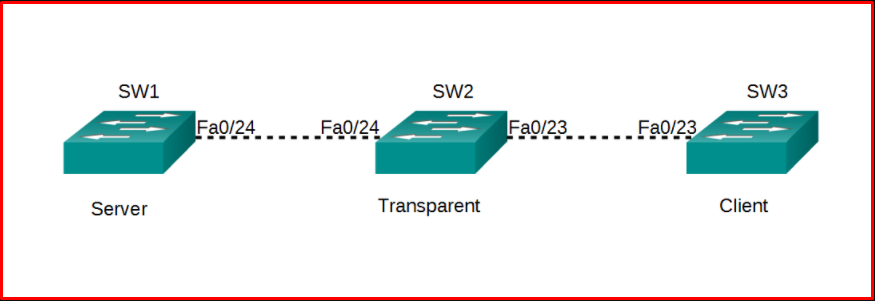
VTP Working Mode
There are three kinds of VTP operating modes: Server, Client, Transparent.
VTP Server Mode: It comes pre-installed on Cisco Catalyst series switches. For each VTP domain, at least one VTP server is needed for adding, removing and configuring VLANs. Every change made on a switch operating in server mode is announced to that VTP domain. Its configuration is stored on NVRAM (Non-Volatile RAM).
VTP Client Mode: These are the switches that receive information from VTP servers, receive and send update information, but cannot make any changes. Its configuration is not stored on NVRAM (Non-Volatile RAM), it is temporary.
VTP Transparent Mode: These are the switches that send incoming VTP information over trunk ports without joining the VTP domain group. The VTP database on them does not transmit the changes that can be made on it from trunk ports. Its configuration is stored on NVRAM (Non-Volatile RAM).