Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is Microsoft’s cloud-based directory and identity management system. It has many different features such as working with iOS, Mac OS X, Android and Windows operating systems, single sign-on (SSO) in the cloud and on-premises web applications. It is the application used for user, identity management and authorization of all services and services in Iaas, PaaS and Saas structures serving in the Microsoft Azure cloud.
Why Should We Use Azure AD?
With developing technology, the applications we use are becoming more complex. As such, opening the built-in applications out will pose great security risks. For this reason, you can share the new generation services and protocols offered in the most secure way by sharing them with our service on the cloud in order to meet the continuous and developing business needs.
Differences Between Active Directory and Azure Active Directory
While there are many similarities between the Azure AD and Active Directory, there are also many differences. Below are the features that distinguish Azure AD from Active Directory.
- While queries in Active Directory are made as LDAP queries, since Azure AD is HTTP / HTTPS based, queries are made as REST (Representational State Transfer) API.
- Kerberos and NTLM are used for authentication in Active Directory. HTTP / HTTPS protocols such as SAML, WS-Federation and OpenID are used in Azure AD. OAuth is used for authorization.
- Federation Services are available in Active Directory. In addition to these services, Azure AD also includes many third party services.
- Organizational Unit (OU) and Group Policy (GPO) are available in Active Directory. It is not available in Azure AD.

Active Directory (AD DS) resides on a Windows Server-based physical or virtual server. Although Active Directory is a component in the Windows Active Directory package, it is primarily known as a directory service. Active Directory can be deployed and managed on an Azure virtual machine. However, if the Infrastructure As A Service (IaaS) structure is used in the cloud environment and the distribution of workloads is aimed, it is recommended to use Azure AD for this.
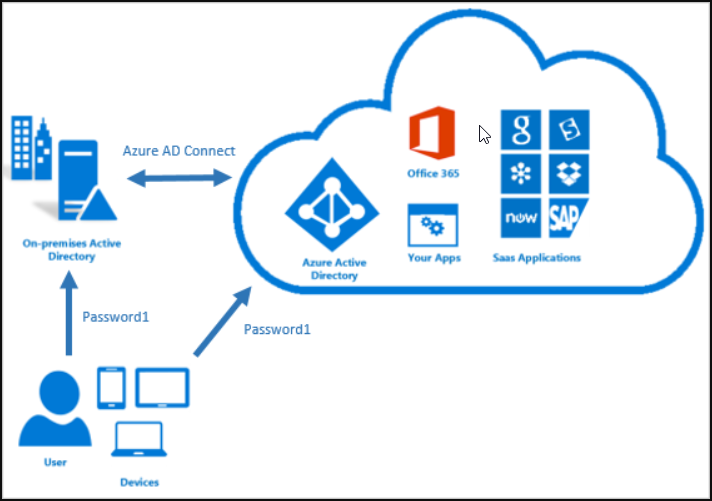
You can see the picture below to compare what both services offer you.

Azure AD Features
You can look at the following useful features of the Azure Active Directory (ADD).
- AAD is primarily designed for Internet-based applications using an identity solution and HTTP (port 80) and HTTPS (port 443) communication.
- AAD users and groups can be created, but there are no Organizational Units (OU) such as Windows Server Based Active Directory and Group Policy Object architecture for management.
- AAD does not support inclusion within the server and computer domain.
- AAD cannot make direct queries via LDAP, instead, it uses REST API over HTTP and HTTPS.
- AAD does not use Kerberos authentication but instead happens over HTTP or HTTPS for authentication. It uses the SAML, WS-Federation and Open ID Connect protocols used in the backend (OAuth for Authorization).
- AAD is in the federation with many third-party applications. With your Azure Active Directory (ADD) password, you can access the applications you are federated with. Sample; Facebook, Dropbox for Business, SalesForce




