The Washington Post, one of the largest and oldest newspapers in the United States, reported on December 13, 2020, that many government agencies, including the US Treasury Department, were compromised and a large number of confidential data stolen through SolarWinds Orion software. A few days before that date, FireEye, one of the largest cybersecurity companies in the USA, announced that it was hacked and its red team tools were stolen, possibly as a result of a “state-sponsored” operation.
It was determined that the Russian-backed APT group known as APT29/Cozy Bear was behind this successive attack and SolarWinds’s update servers were used in the attacks.
With more than 1.5 million active users worldwide, SolarWinds provides firmware and services such as network and system infrastructure management, virtualization management, security management, database management. SolarWinds can monitor almost any system and device in typical networks, this feature is well before an attacker perspective. Any system with a certain level of administrator rights in your environment can be vulnerable.
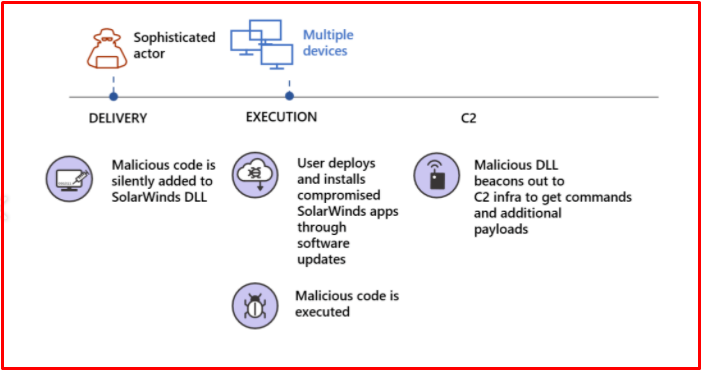
In a recent statement, FireEye announced that they identified a new global attack campaign that was distributed via a software update. The actors behind the campaign are followed as UNC2452. The designated campaign was found to distribute the malware called SUNBURST through updates to the SolarWinds Orion network monitoring product, which is the widely used IT infrastructure management software.
According to analysis, the attacks believed to have been carried out as part of this campaign include some common elements:
- Malicious SolarWinds update: It has been detected that malicious code can be added to legitimate software updates for Orion software that allows an attacker to remotely access the victim’s environment.
- Light malware footprint: It has been found that limited malware is being used to perform the task while avoiding detection.
- Prioritize privacy: It has been detected that careful action has been taken to adapt to normal network activity.
- High OPSEC: It has been found that exploring has been done patiently and using tools that are difficult to attribute.
SUNBURST Backdoor Overview
SolarWinds.Orion.Core.BusinessLayer.dll is a component of the Orion software framework that communicates with third-party servers via HTTP and includes a backdoor. The Trojan version of the SolarWinds Orion plugin was named SUNBURST.
The malware was found to execute commands called “Jobs”, which, after two weeks of inactivity, include the ability to transfer files, execute files, profile the system, restart the machine, and disable system services. The malware has been found to hide network traffic as the Orion Improvement Program (OIP) protocol, keeping the discovery results in legitimate configuration files, thereby adapting to classic SolarWinds activity and preventing detection. It was also found that it uses multiple cloaked block lists to identify forensic and anti-virus tools that work on the basis of backdoor, processes, services and drivers.

SolarWinds Security Advice
According to a security proposal published by SolarWinds, the attack was found to target versions 2019.4 to 2020.2.1 of the SolarWinds Orion Platform software released between March and June 2020. Users are urgently advised to upgrade to 2020.2.1 HF 1 version to Orion Platform release.
Stating that the details of the attack are currently being investigated in coordination with FireEye and the US Federal Bureau of Investigation, the company announced that the 2020.2.1 HF version, which replaces the compromised component on December 15 and provides a few extra security considerations, will be released as soon as possible.
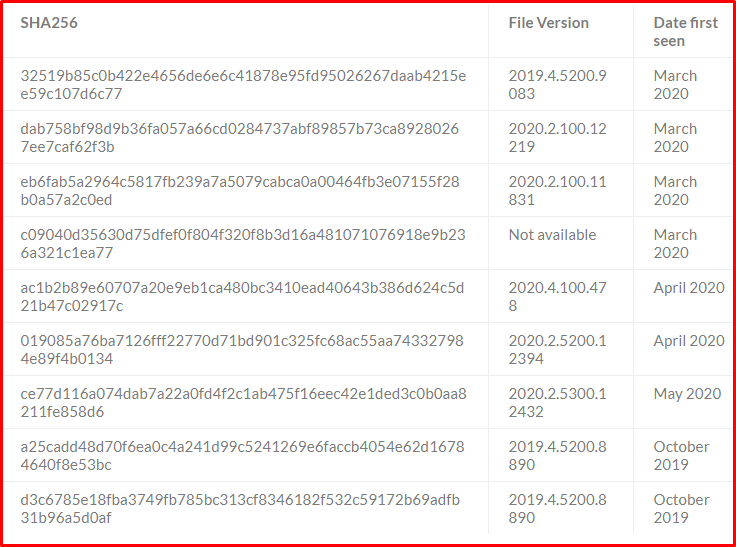
Malicious Examples of the SolarWinds.Orion.Core.BusinessLayer.dll File
These indicators should not be considered alone for the observed activity. It is useful to keep track of the new IOCs and TTP that are said to belong to the attack.